v1.1.0
Features
Source metadata
EventBridge Atlas now allows you to write a description and list of maintainers for each source on your bus.
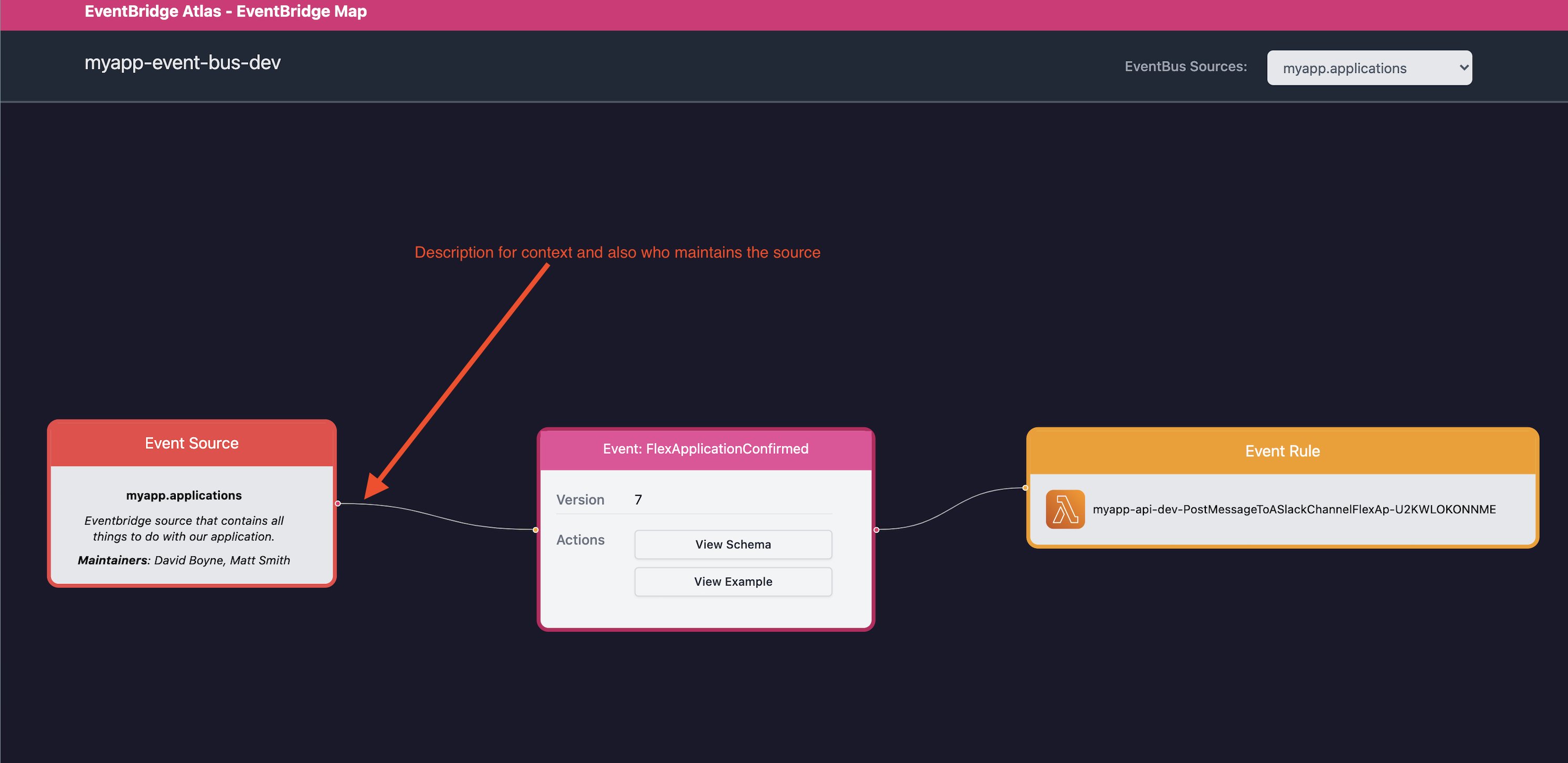
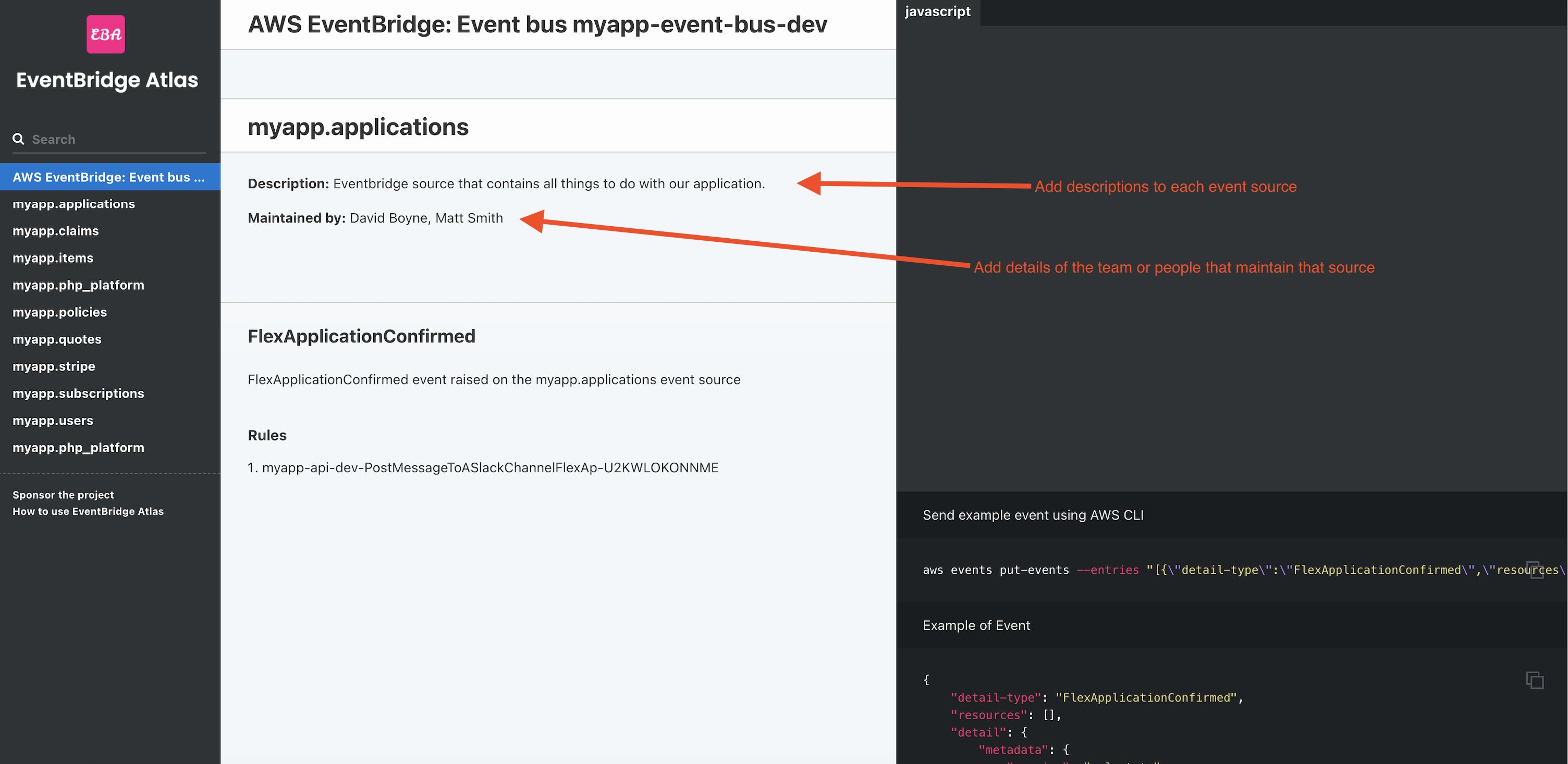
Why
This feature is another way you can help give extra context to team members about why your event sources may exist and their boundaries within your system. Some larger organisations also split domains by source, so you may have different people/teams managing the sources, you can now define who owns them and maintains them.
How to get started
When you run npm run generate-eventmetadata this will populate your /data folder with all your events.
Generate metadata will now also put a new file in your source directorys called source-metadata.json. This file will contain the description and maintainers. Running npm run generate-eventmetadata will populate a template for you.
Example
{
"description": "Here is a description of my source",
"maintainers": ["David Boyne"]
}
File can be found in /data/{source}/source-metadata.json.
If you don't wish to run the generate script again you can simply just add the source-metadata.json file in the correct location.
Everything here is optional, and the application will continue to work even if you don't have any source-metadta files.